Chat History
EVI records detailed conversation histories, enabling developers to review and analyze past chat sessions. This guide introduces Chats and Chat Groups, and explains how to retrieve chat transcripts, expression measurements, and reconstructed audio.
If data retention is disabled, chat history will not be recorded. This means past chat data and audio reconstructions will no longer be accessible or retrievable.
Chats vs Chat Groups
EVI organizes conversation history into two levels: Chats and Chat Groups.
- Chats represent individual sessions, beginning when a WebSocket connection is established and ending when it closes. Each chat contains the messages and events recorded during that session.
- Chat Groups link related chats to maintain continuity across multiple sessions. A group can contain one or more chats, allowing conversations to persist even when users disconnect and reconnect.
By default, a new chat session creates a new chat group. If the session resumes a previous conversation, the new chat is added to the existing chat group, preserving the full interaction history and context across sessions.
Fetching Chats & Chat Groups
Each Chat has a unique chat_id and a chat_group_id that links it to its corresponding Chat Group. Similarly, each
Chat Group has its own ID, allowing you to retrieve individual sessions or entire sequences of related interactions.
Chat ID
Use the list Chats endpoint to fetch chats. The returned chat_id
can be used to fetch chat details or resume a previous session.
Chat Group ID
Every chat includes a chat_group_id that identifies the group it belongs to. To fetch chat groups directly, use the
list Chat Groups endpoint. This is useful for
retrieving all chats that are part of an ongoing conversation.
From chat_metadata
You can also extract both IDs at the start of every session via the chat_metadata message. This is useful for associating downstream actions or data with the active chat session.
Viewing Chats in the Platform UI
You can also explore chat history and retrieve Chat IDs directly through the Platform UI:
-
Visit the Chat history page to see a paginated list of past chats. Each entry displays key information such as the Chat ID, timestamp, event count, and duration.
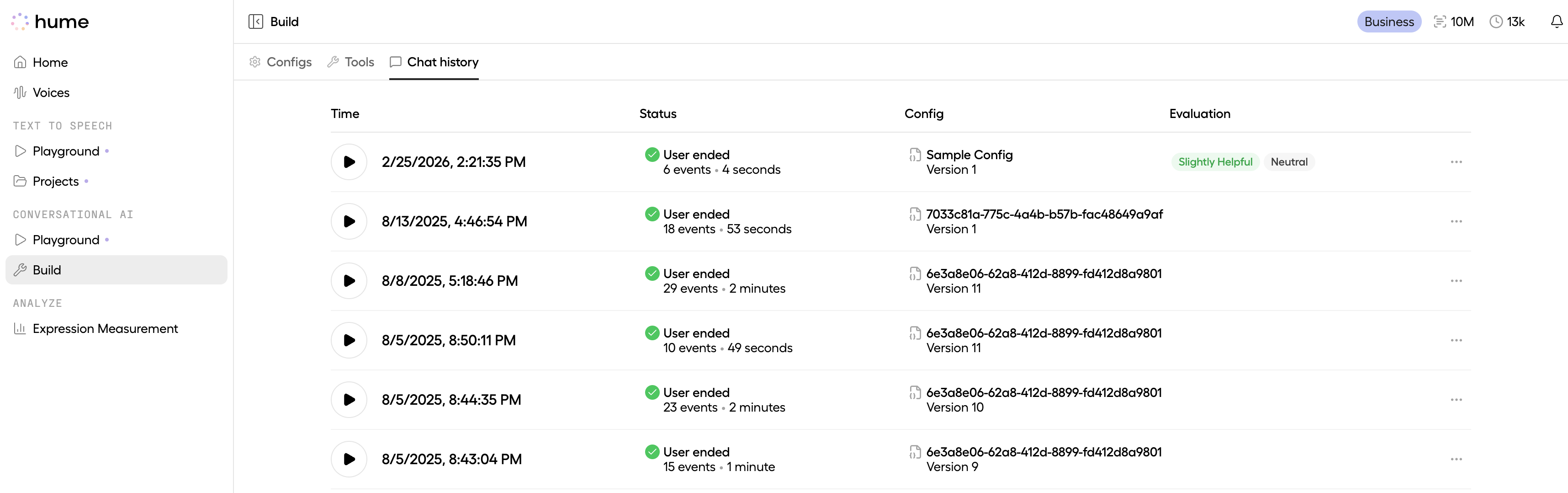
-
Click “Open details” on any chat to view its full details. The chat details page includes the Chat ID, Chat Group ID, start and end timestamps, duration, status, associated Config ID (if applicable), and a paginated list of recorded chat events.
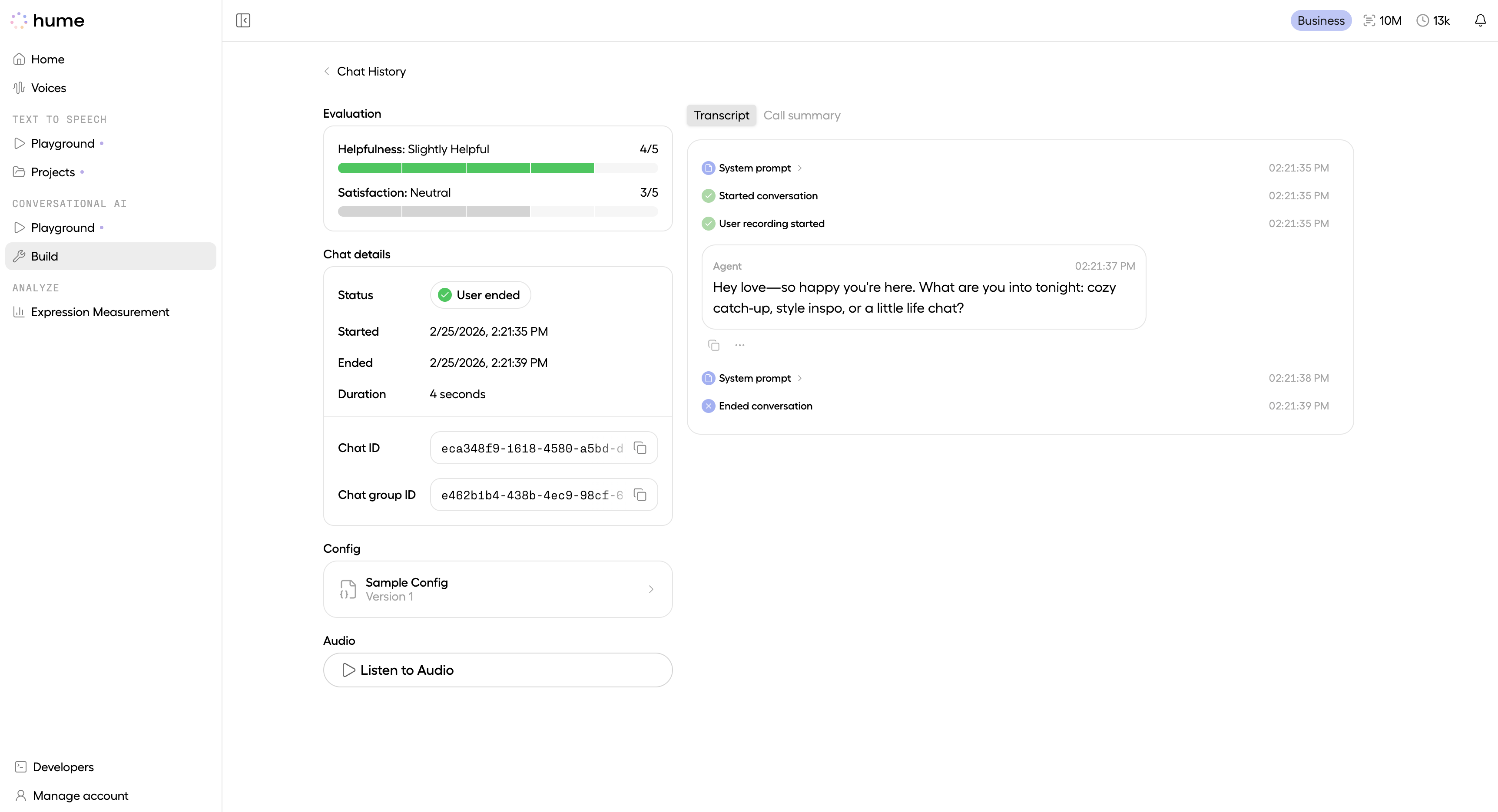
Chat Events
Each Chat consists of a sequence of predefined events that represent everything that occurred during the session.
The table below outlines each event type and its purpose.
Fetching Chat Events
The Chat Events API lets you retrieve detailed event data for a specific Chat or an entire Chat Group. Each event represents a message, action, or system signal recorded during a session. You can use these endpoints to reconstruct transcripts, analyze interactions, and extract emotion predictions.
Fetching events for a Chat
Use the /chats/{chat_id}/events endpoint to fetch events for a single Chat:
Fetching events for a Chat Group
Use the /chat_groups/{chat_group_id}/events endpoint to fetch events across Chats within a Chat Group:
Parsing Chat Events
Chat events provide a structured record of each conversation, capturing both transcribed messages and expression measures over time. Use this data to generate readable transcripts, analyze sentiment, and build visualizations of user–assistant interactions.
The following examples show how to work with chat event data using the Hume SDKs:
Parse chat events, transcripts, and emotions with the TypeScript SDK.
Extract transcripts and emotion data using the Python SDK.
Chat transcription
Conversation transcripts can be reconstructed from USER_MESSAGE and AGENT_MESSAGE events. These events include the
speaker’s role, timestamp, and message text, allowing you to format the dialogue into a readable script.
The following example extracts a chat transcript from a list of events and writes it to a text file:
Expression measurement
Expression measurement predictions are stored in the USER_MESSAGE events under the emotion_features property.
These predictions provide confidence levels for various emotions detected in the user’s speech.
For example, you might want to gauge the emotional tone of a conversation to better understand user sentiment. This information can guide customer support strategies or highlight trends in the expression measurement predictions over time.
The following example calculates the top 3 emotions from the USER_MESSAGE events by averaging their emotion scores
across the Chat session:

